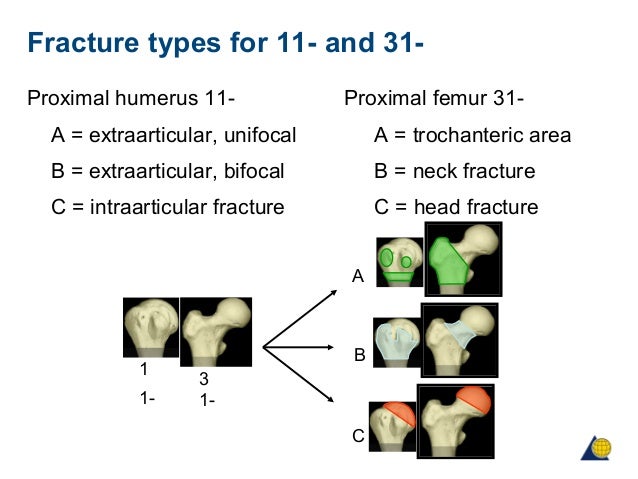
Und/oder Patella, liegende Prothese proximal oder distal, Adipositas permagna) Dies beinhaltet gemäss AOKlassifikation Indikationen – Frakturen des Typs 33A1 bis A3 – Frakturen des Typs 33C1 bis C31 – Frakturen des Typs 32A bis C 2 Kontraindikationen – Frakturen des Typs 33B, 33C32 und 33C33The AO classification divides proximal humeral fractures into three groups, A, B and C, each with subgroups, and places more emphasis on the blood supply to the articular surface 1,230 21 Stürmer K M, Dresing K
Ao Ota Fracture Classification Pdf Newmarket
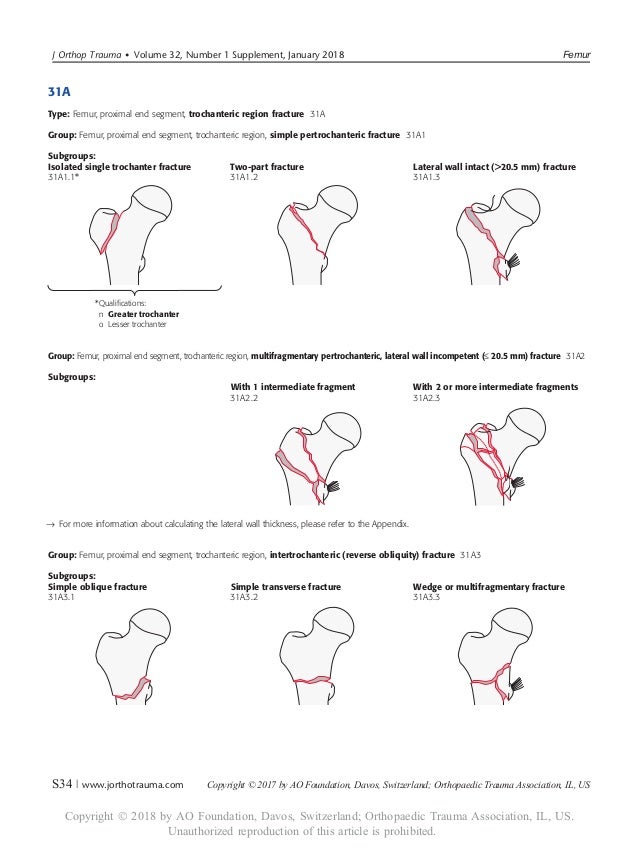
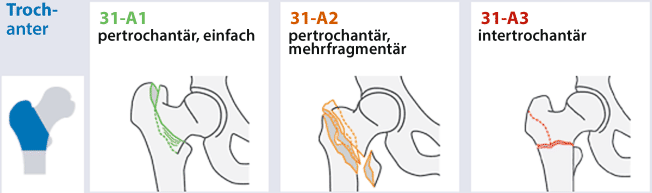
Ao klassifikation femur proximal
Ao klassifikation femur proximal-MUSIC Proximal femur fractures can cover femoral head fractures, femoral neck fractures, pertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures It is important to consider anatomical basic principles once again The proximal femur has a callumcaputJul 02, According to the Müller AO Classification, the proximal femur is identified by the number 31



Ao 18
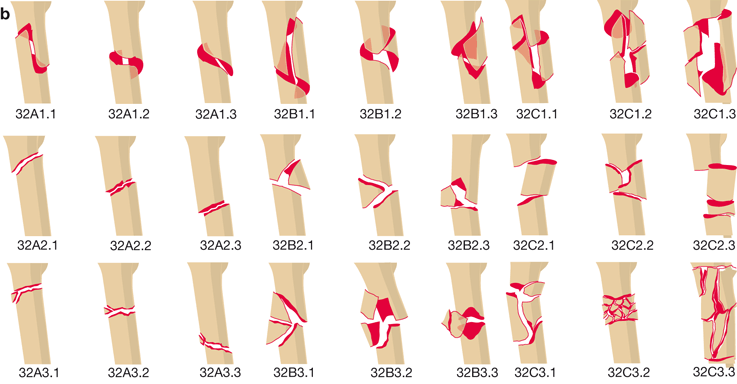
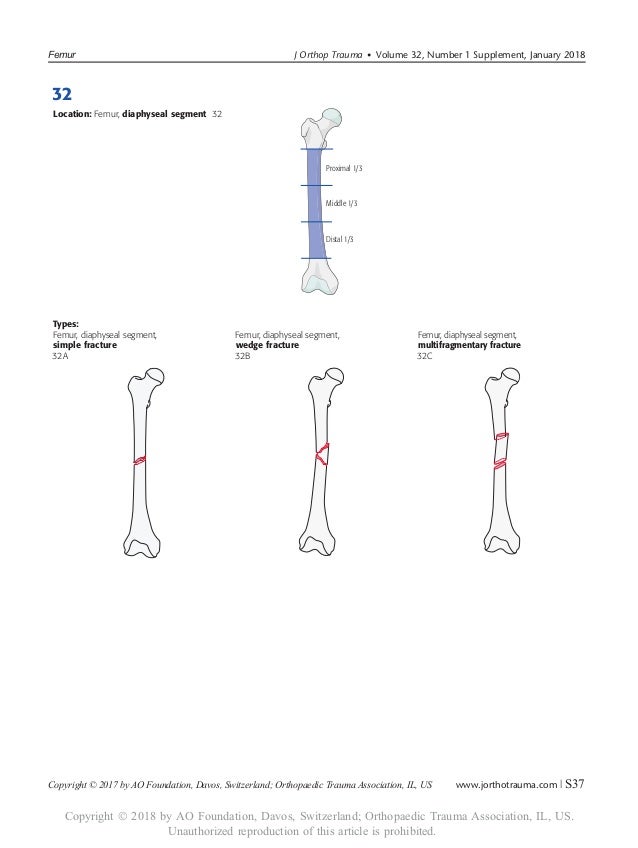
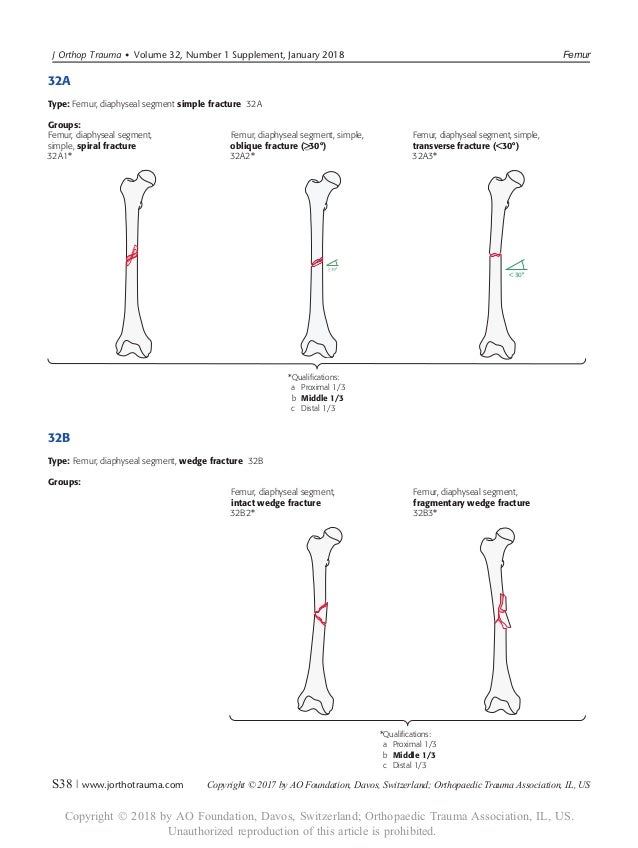
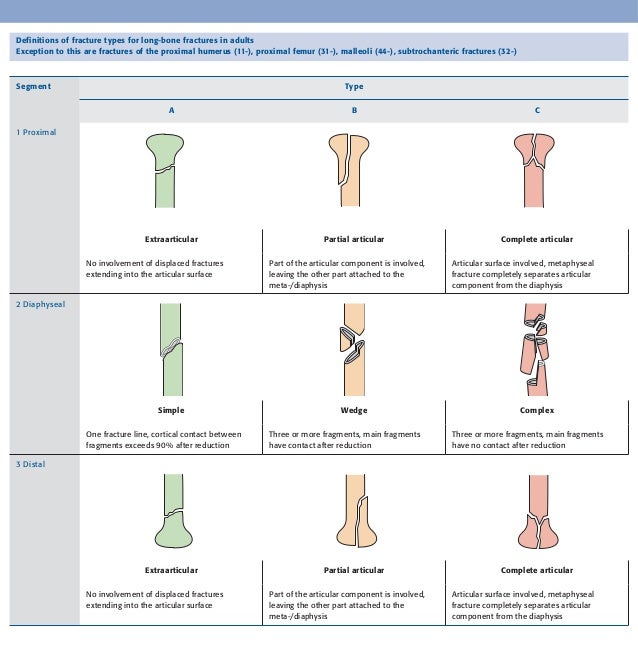
The proximal and distal segments of long bones are defined by a square the sides of which have the same length as the widest part of the epiphysis (exceptions 31 and 44) Alphanumeric structure of the Müller AO Classification of Fractures—Long Bones for adults Example 32B2 3 femur 2 diaphyseal BApr 02, 16Figure 44 illustrates a proximal femur study in which the femoral shaft was not straight or parallel to the edge of the table This proximal femur is still abducted The positioning should be corrected by moving the leg slightly toward the center of the table The need to adjust the position of the femoral shaft based on the scan image shouldJul 17, 15Figure 3 Computergenerated image demonstrates the vascular anatomy of the proximal femur Blood flow to the proximal femur is supplied primarily by the branches of the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries Supplemental flow to the femoral head is supplied by the artery of the ligamentum teres, a branch of the obturator artery
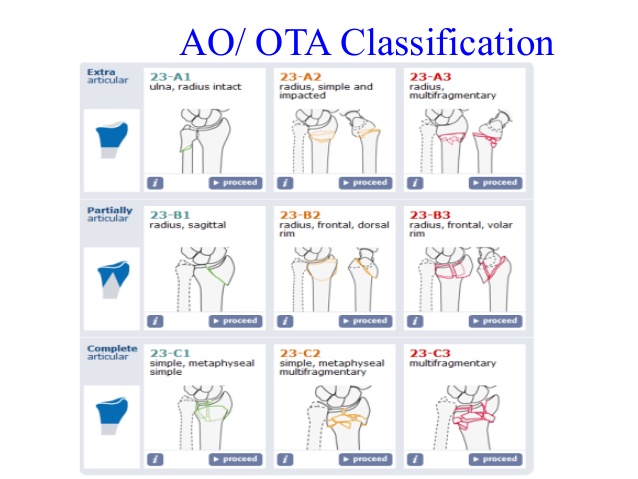
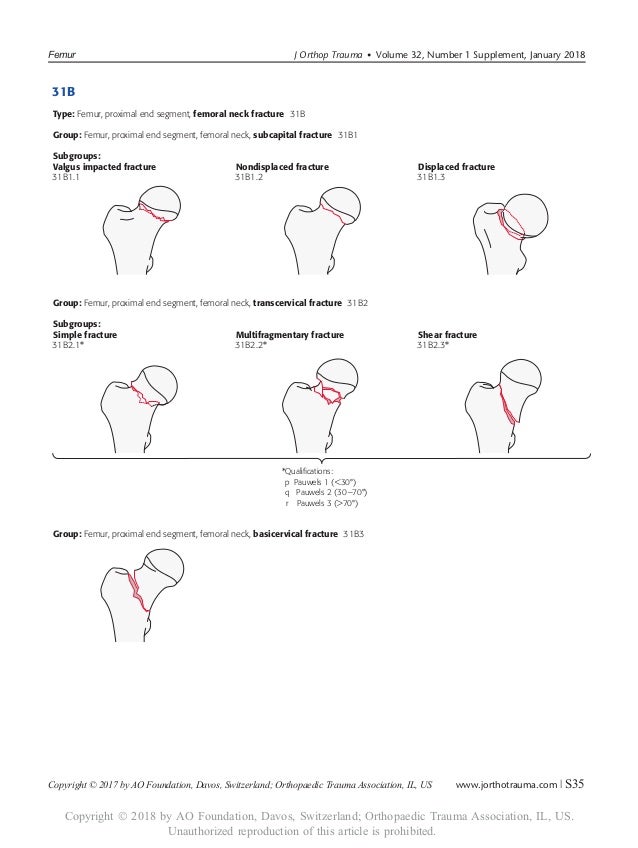
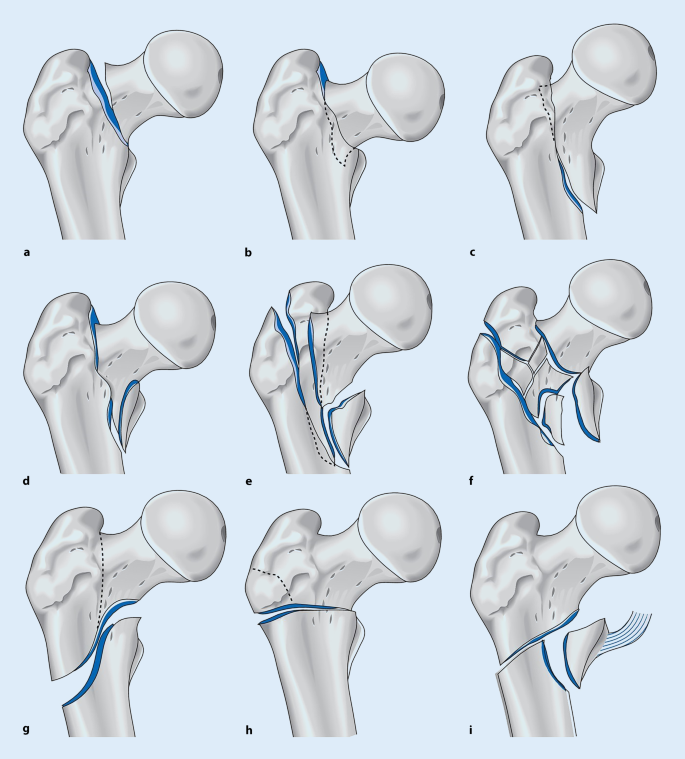
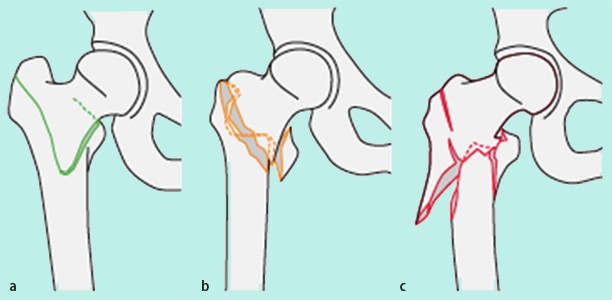
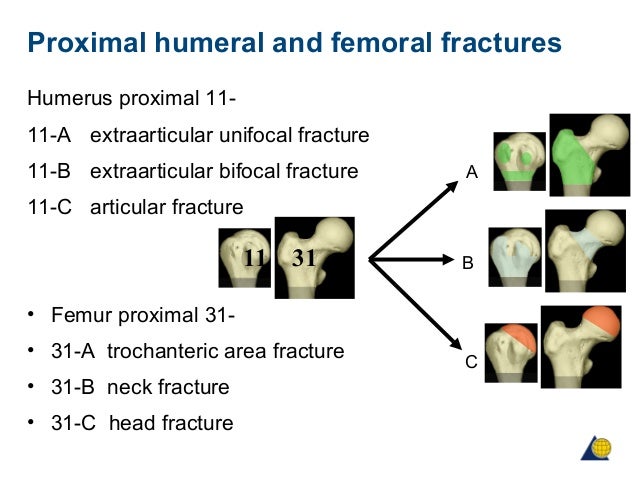
IIIB Threepart spiral fractures of the proximal third of the femur, in which the third part is a butterfly fragment Type IV Comminuted fractures with four or more fragments Type V Subtrochantericintertrochanteric fractures, including any subtrochanteric fracture with extension through the greater trochanter07 Available learning resourcesType B fractures of the proximal femur are fractures of the femoral neck 31C articular fracture, head Type C fractures of the proximal femur are fractures of the head of the femur Adapted from Rüedi TP, Buckley RE, Moran CG AO Principles of Fracture Management 2nd ed Stuttgart New York Georg Thieme Verlag;
Inclination angle between the head and neck and the femoral body Further, there is a 15°Congenital abnormalities of the femur vary from a deficiency of the entire femur with abnormal development of the pelvis to a hypoplastic femur of normal configuration Previous classification systems that have focused on either congenital coxa vara, hypoplastic femur, or proximal femoralOder Patella, liegende Prothese proximal oder distal, Adipositas permagna) Dies beinhaltet gemäss AOKlassifikation Indikationen – Frakturen des Typs 33A1 bis A3 – Frakturen des Typs 33C1 bis C31 – Frakturen des Typs 32A bis C Kontraindikationen – Frakturen



Ao Classification




Proximal Femur Fractures Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets
Proximal femur includes the femoral head, neck and the region 5cm distal to the lesser trochanter There is a 125°–130°Jun 17, 21Landmarks Proximal end The proximal end of the femur includes the femoral head;AO Pediatric Comprehensive Classification of LongBone Fractures (PCCF) by the AO Pediatric Classification Group and AO Clinical Investigation and Documentation (07) to the proximal femur, where metaphyseal fractures are located between the physis of the head and the intertrochanteric line



Per Und Subtrochantare Femurfrakturen Springerlink



Ao 18
The proximal femur is an exception Its metaphysis is not defined by a square but located between the growth plate and the subtrochanteric line If the center of the fracture lines is located within the above mentioned square, it is a metaphyseal fractureSep 03, 16Operations on the femur are extremely common The lateral approach to the proximal femur, which is used to treat the growing number of patients who have intertrochanteric hip fractures, is the most frequently used approach in orthopaedic surgery The four basic approaches to the femoral shaft, the lateral, posterolateral, anterolateral, and anteromedial, allAOKlassifikation der Wirbelsäulen## (AO 5053) Die 5 der Wirbelsäule bekommt 2 weitere Ziffern, die mit einem Punkt getrnnt sind die Ziffern 1, 2 bzw 3 für HWS, BWS bzw LWS und nach dem Punkt die Nummer des Wirbelkörpers




File Hoftfraktur Indelning Png Wikimedia Commons



The Epidemiology Of Adult Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures In A Central London Major Trauma Centre Over Five Years
The femur is a big bone, and the proximal part of the femur has a number of important parts that make it part of the hip joint and the muscles involved thereClassification Type I Fracture line extends upwards and outwards from the lesser trochanter (stable) Type I fractures can be further subdivided as Type Ia Undisplaced twofragment fracture Type Ib Displaced twofragment fracture Type Ic Threefragment fracture without posterolateral support, owing to displacement of greater trochanter fragment Type Id Threefragment fractureProximal, shaft and distal In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the femur – its attachments, bony landmarks, and clinical correlations



Femur Proximal Aocms



Muller Ao Classification
The AO has established specialty areas for trauma, spine, craniomaxillofacial, veterinary and reconstructive surgery The AO clinical divisions and clinical unit continually redefine the stateoftheart in their fields, maintaining activities in research, development, clinical investigation and education Since the AO was founded, more thanC2 Simple articular, wedge or multifragmentary metaphyseal Open subtypes (2)A comparison of the long gamma nail with the sliding hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA 31 fractures of the proximal part of the femur a prospective randomized trial Author Barton TM, Gleeson R, Topliss C, et al J Bone Joint Surg Am 10 Apr;92(4)7928



Proximale Femurfraktur Und Insuffizienzfrakturen Im Alter Springerlink




Ao 18
Wiederherstellung der Funktion und Anatomie des Proximalen Femur 4 (AOKlassifikation 31, 31A3), subtrochantäre Femurfrakturen (AOKlassifikation 32A1), Headsplit fractures of the proximal humerusHeadSplitFrakturen des Proximalen Humerus 11A femoral fracture is a bone fracture that involves the femurThey are typically sustained in highimpact trauma, such as car crashes, due to the large amount of force needed to break the bone Fractures of the diaphysis, or middle of the femur, are managed differently from those at the head, neck, and trochanterJun 01, 1999The Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen (AO/ASIF) therefore designed a new intramedullary device, the proximal femoral nail (PFN), which during a handling study was tested in 4 European clinics Within one year 191 proximal femoral




The Ao Ota Classification Of The Extracapsular Proximal Femur Fractures Download Scientific Diagram



Ao Klassifikation Der Frakturen Fur Den Handheld
Einzelkodes der PAEGKlassifikation In Anlehnung an die AOKlassifikation fr Erwachsene werden die langen Rhrenknochen mit 14 bezeichnet (1 Humerus, 2 Radius/Ulna, 3 Femur, 4 Tibia/ Fibula,Jan 02, 15Femoral osteotomy is a surgical procedure that is performed to correct specific deformities of the femur – the long bone in the upper leg – and the hip joint Orthopedic surgeons perform the operation, which involves cutting the bone, in order to realign it and restore a more normal anatomy, thereby addressing or preventing problems relatedAOKlassifikation der AO Foundation Wenn ihr die Darstellung auf einer einzigen Seite bevorzugt, wird die AOKlassifikation von HH Jend auch gut auf seiner HTMLSeite für Handhelds zusammengefasst CMF, proximal femur, distal femur, patella, tibial shaft (members only) Femoral shaft (free module) Access all dog modules here AO Surgery



Fraktur Proximala Ulna




Classifications Of Proximal Humeral Fractures Rotator Cuff
The femur is the only bone in the thigh and the longest bone in the body It acts as the site of origin and attachment of many muscles and ligaments, and can be divided into three parts;There are a number of classification systems for intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur, but none has been shown to be practical with satisfactory reproducibility and accurate predictive value We have investigated the AO classification and evaluated intra and interobserver accuracy and its value in predicting treatment and outcomeType Reference Material Author/Contact Not Available Institution AONA Primary Subject/Category OCOSH Classification Trauma Fractures Femur Fractures Hip Fractures Orthopedic Topics Trauma Hip Language English Submitted by admin Hits 2161 Added Mon Feb 04 02 Last Modified Mon Jul 02 07



Classification Of Children S Fractures



Classification Of Children S Fractures
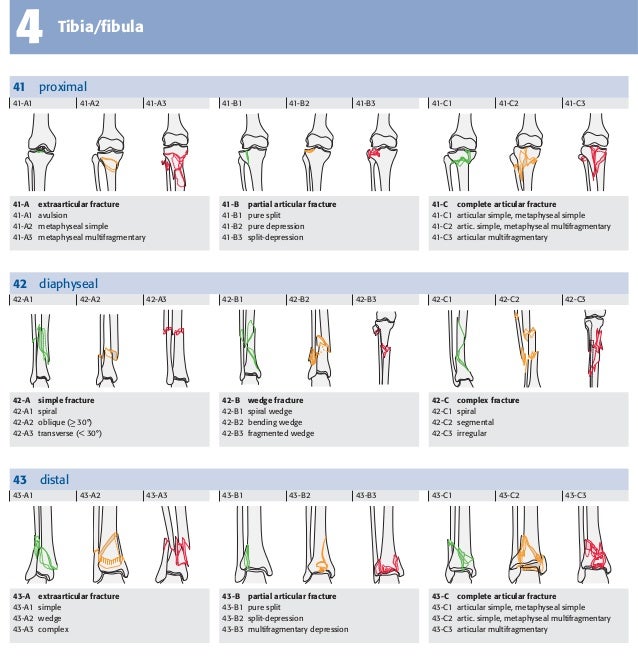
THA Periprosthetic Fracture THA Periprosthetic Fractures are a complication of a total hip prosthesis with increasing incidence as a result of increased arthroplasty procedures and highdemands of elderly patients Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs of the affected hip and ipsilateral femurThe AO/ASIFproximal femoral nail (PFN) a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures Injury 1999;The location within the bones is the proximal end segment (1), diaphyseal segment (2), and, distal end segment (3) The end segment consists of the epiphysis and metaphysis The metaphyseal end segment is determined by a square whose sides are the same length as the widest part of the visible epiphyseal growth plate ( Fig 3 ) 11 For the radius



Per Und Subtrochantere Femurfrakturen Springerlink
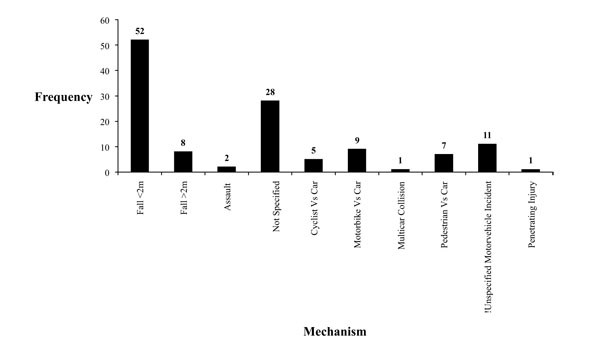



The Epidemiology Of Adult Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures In A Central London Major Trauma Centre Over Five Years
A femoral fracture is a fracture of the femur (thigh bone) A femoral shaft fracture is defined as a fracture of the diaphysis occurring between 5 cm distal to the lesser trochanter and 5 cm proximal to the adductor tubercle occurs by chronic, repetitive activity that isClassification of proximal femoral deficiency (PFFD) can be complicated and numerous such classifications have been proposed For a discussion of the condition refer to the article proximal focal femoral deficiency One of the simplest and most widely used is that proposed by Aitken 1 which is based on the anatomic relationship between the acetabulum and the proximal end of the femurOsteotomien am proximalen Femur, also dem Segment 31 der AOKlassifikation 5 entsprechend, können bei folgenden Pathologien indiziert sein – rezidivierende Hüftluxationen oder ‑subluxationen, – Femurkopfnekrosen, – Pseudarthrosen, – Deformitäten, – koxofemorale Destruktion Diese unterschiedlichen Pathologien er




Ao Ota Type 31 A Pertrochanteric Fractures 31 A1 Fractures Are Simple Download Scientific Diagram




Olecranon Fractures Trauma Orthobullets
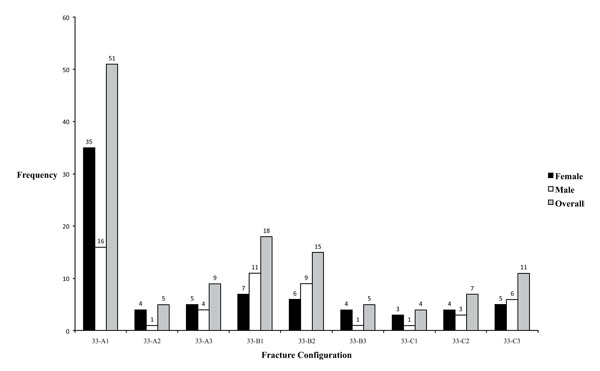
AO/OTA Classification 33 Distal femur • A Extraarticular • B Intraarticular (single condyle) •A1 A3 •B1 B2 C Intraarticular (both •C1 C2 C3 condyles) Anatomy Distal Femur • Physiologic valgus – (59 degrees) • Mechanical axis • Posterior half of both femoral condyles lie posterior to the femoral shaftThe incidence of different AO groups was as follows 48% AO Type A, 39% Type B, and 13% Type C The A3 transverse femoral shaft fracture was the most common, followed by the B2 group with a bending wedge type and an intact butterfly fragment The C1 and C2 groups (spiral and segmental complex fractures) were the least commonFeb 06, 13Up to10%cash backUnstable trochanteric fracture (AO classification 31, 31A3), subtrochanteric fracture (AO classification 32A1), fracture of the femoral shaft in the proximal region




Ao Ota Classification Of Distal Humeral Fractures Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Ao Spine Classification Of Upper Cervical Injuries Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Anteversion angle between the plane passing through the condyles of the femoral head and the femur neckMay 13, Up to10%cash backDie sichere Diagnostik und Klassifikation proximaler Femur und Tibiafrakturen ist zur Festlegung des therapeutischen Vorgehens essenziell In diesem Beitrag werden die aktuellen Standards bezüglich der Bildgebung im Bereich des proximalen Femurs und der Tibia dargestellt sowie die Wertigkeit verschiedener KlassifikationssystemeWe help you diagnose your Proximal femur case and provide detailed descriptions of how to manage this and hundreds of other pathologies




Garden Classification Of Hip Fractures Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Hip Fractures Amboss
The head of the femur is a roughly spherical structure that sits superomedially and projects anteriorly from the neck of the femur The smooth convexity of the femoral head is disrupted on the posteroinferior surface by




The Ao Classification System Of Proximal Femur Fractures Reproduced Download Scientific Diagram



Subtrochanteric Femur Fractures Radiology Key



Pertrochantare Femurfrakturen Beim Geriatrischen Patienten Springerlink



Ao 18




The Use Of Upper Limb External Fixation In Paediatric Trauma Injury




Ao Ota Fracture Classification Pdf Newmarket




The Rule Of The Square The Proximal And Distal Segments Of Long Bones Download Scientific Diagram




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fractures Download Table




Abb 1 8 Aoklassifikation Fur Subtrochantare Femurfrakturen Ao Download Scientific Diagram




Hip Fractures Amboss
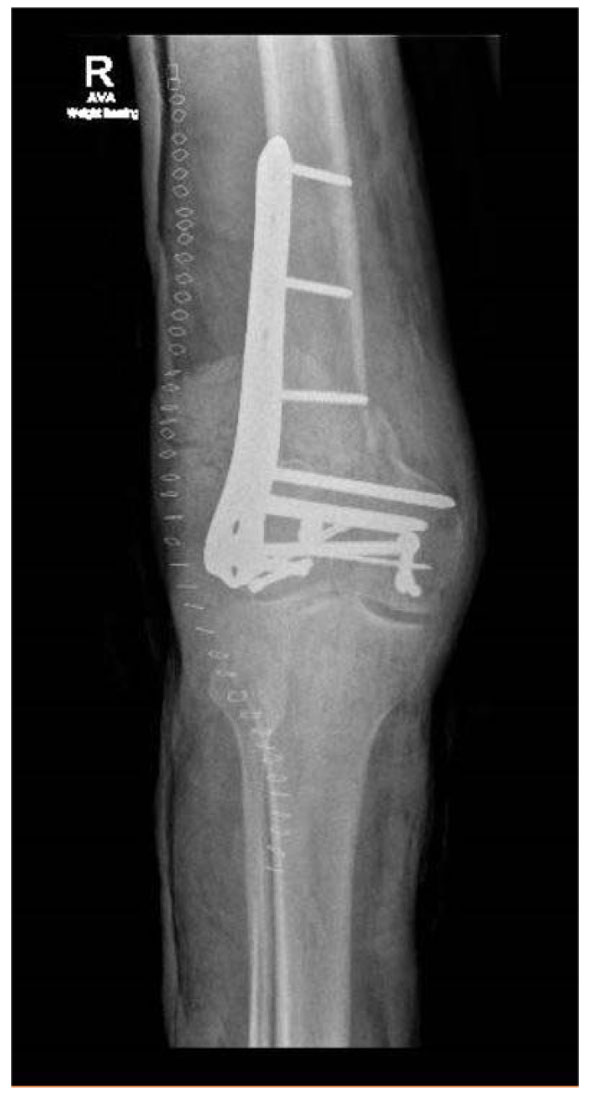



The Epidemiology Of Adult Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures In A Central London Major Trauma Centre Over Five Years




Ao Spine Classification Of Thoracolumbar Injuries Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
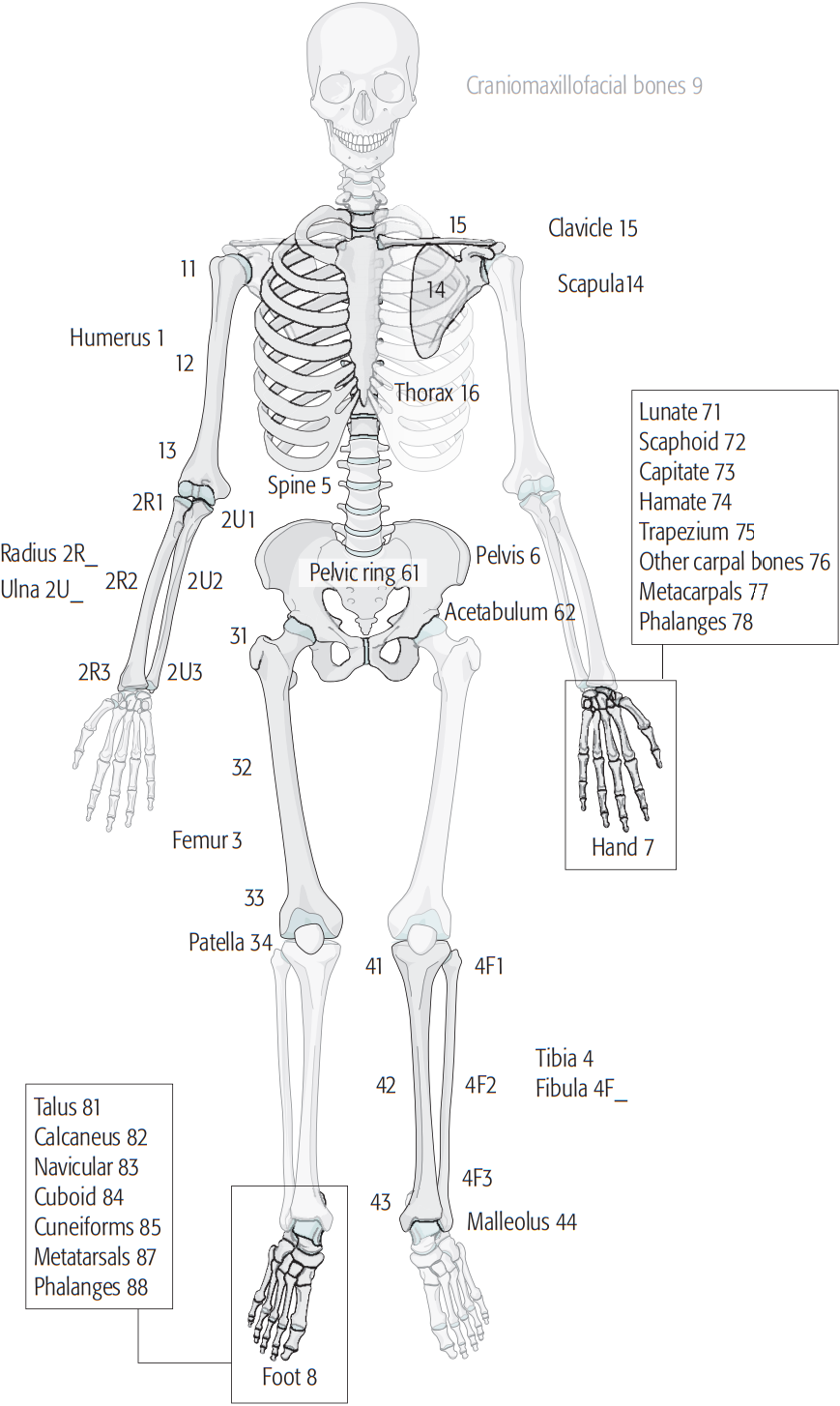



Muller Ao Classification Of Fractures Wikipedia
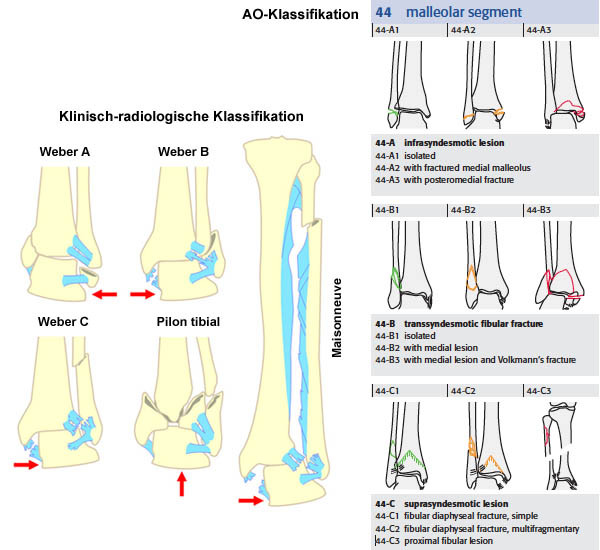



Radiosurf



Classification Of Children S Fractures




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fractures Download Table




Proximal Femur Fractures Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets




Classification Of Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures According To The Ao Download Scientific Diagram




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fracture Ao Ota Classification Download Scientific Diagram
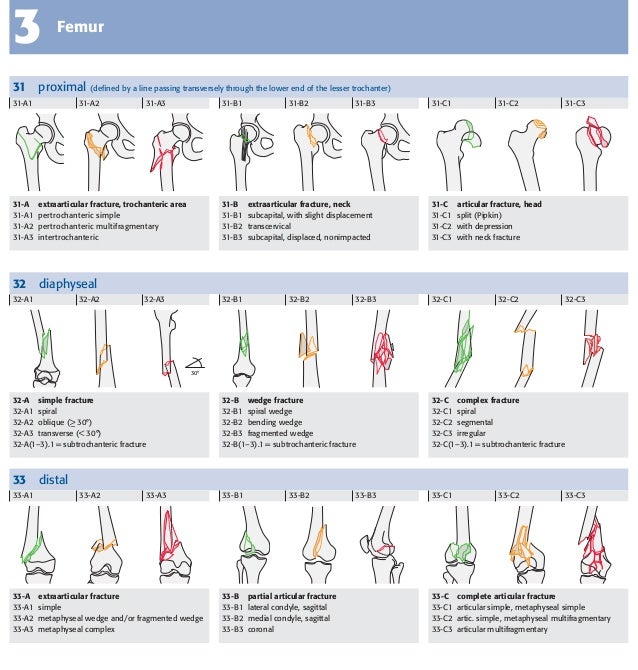



Muller Ao Classification




Clasificacion Ao 07 Clinical Trial Scientific Method



Ao Classification




Frakturen Der Trochanterregion Frak Eref Thieme




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fracture Ao Ota Classification Download Scientific Diagram



Ao Klassifikation Der Frakturen Fur Den Handheld




Klassifikation Eref Thieme



Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fracture Ao Ota Classification Download Scientific Diagram




Ao Klassifikation Der Langen Rohrenkn Eref Thieme




Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube




Pdf Muller Ao Classifi Cation Of Fractures Long Bones Carlos Durao Academia Edu




The Epidemiology Of Adult Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures In A Central London Major Trauma Centre Over Five Years




Winquist Classification Of Femoral Shaft Fractures Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
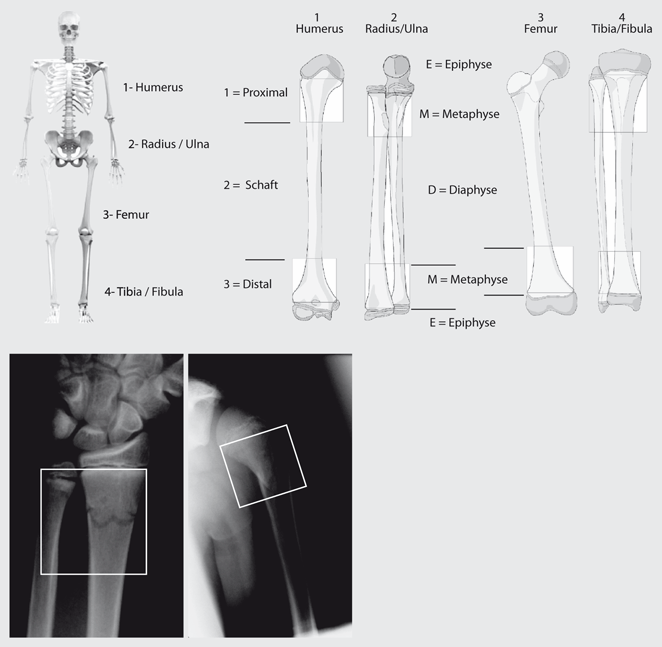



Figure 2 Klassifikationen Von Frakturen Im Kindesalter Springerlink




Proximal Femur Fractures Pediatric Pediatrics Orthobullets




Radiographs Showed An Ao Ota Classification 31 A3 3 Seinsheimer Download Scientific Diagram



The Epidemiology Of Adult Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures In A Central London Major Trauma Centre Over Five Years




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fracture Ao Ota Classification Download Scientific Diagram




Abb 1 8 Ao Klassifikation Distaler Femurfrakturen Ao Download Scientific Diagram




Ao Classification




Abb 1 8 Ao Klassifikation Distaler Femurfrakturen Ao Download Scientific Diagram



Ao 18
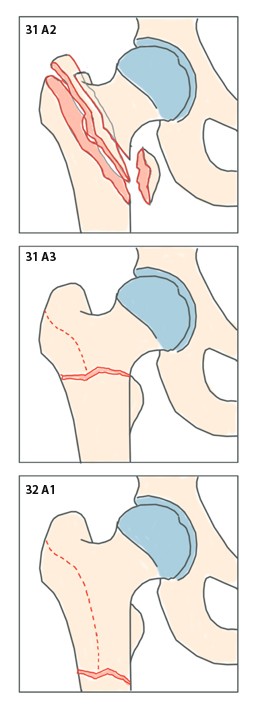



Osteosynthese Von Per Und Subtrochantaren Femurfrakturen Mit Dem Proximalen Femurnagel Springerlink



Classification Of Children S Fractures



Classification Of Children S Fractures



Classification Of Children S Fractures




Pdf Assessment Of The Ao Classification Of Intracapsular Fractures Of The Proximal Femur Semantic Scholar



Muller Ao Classification




Ao Klassifikation Der Langen Rohrenkn Eref Thieme
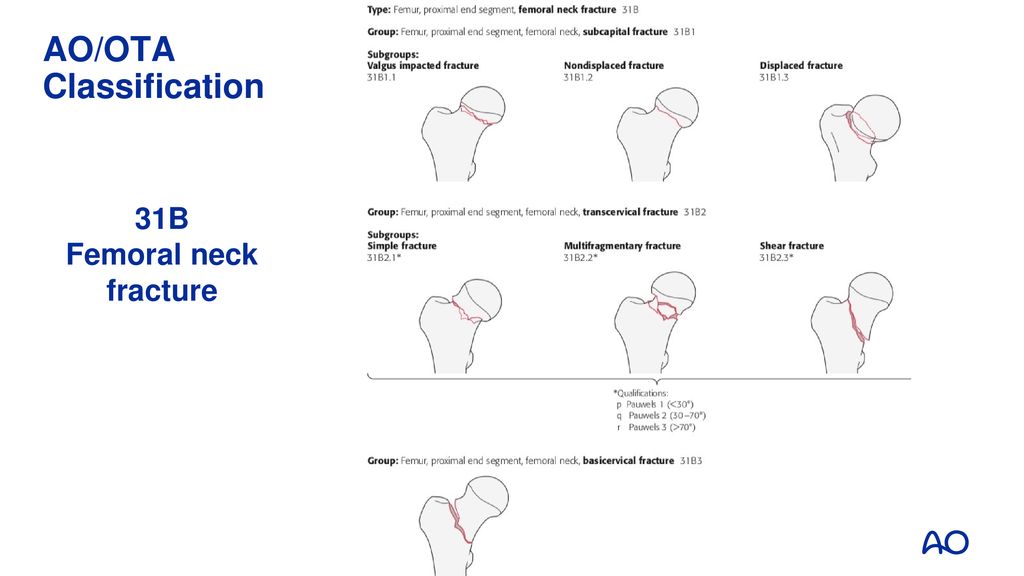



Femoral Neck Fractures Different Patients Different Problems Ppt Download




Ao Dialogue 2 07 By Ao Foundation Issuu



Ao Klassifikation Der Frakturen Fur Den Handheld




Aoota Classification 18 Poster Limbs Anatomy Human Anatomy




Ao Ota Classification Of Proximal Femur Fractures Download Table



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿